Lip cancer is a type of mouth or oral cancer affecting the lips, including the skin, the tissues inside the lips, or the glands that produce saliva. Most lip cancers are squamous cell carcinomas, which means they begin in the thin, flat cells in the middle and outer layers of the skin called squamous cells. It often looks like a mouth sore that won’t heal.
What are the symptoms of Lip Cancer?
Lip cancer can occur anywhere on the upper or lower lip, but it commonly affects the lower lip. This type of cancer is not very common, but it can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated in its early stages. Here are 5 symptoms of lip cancer.
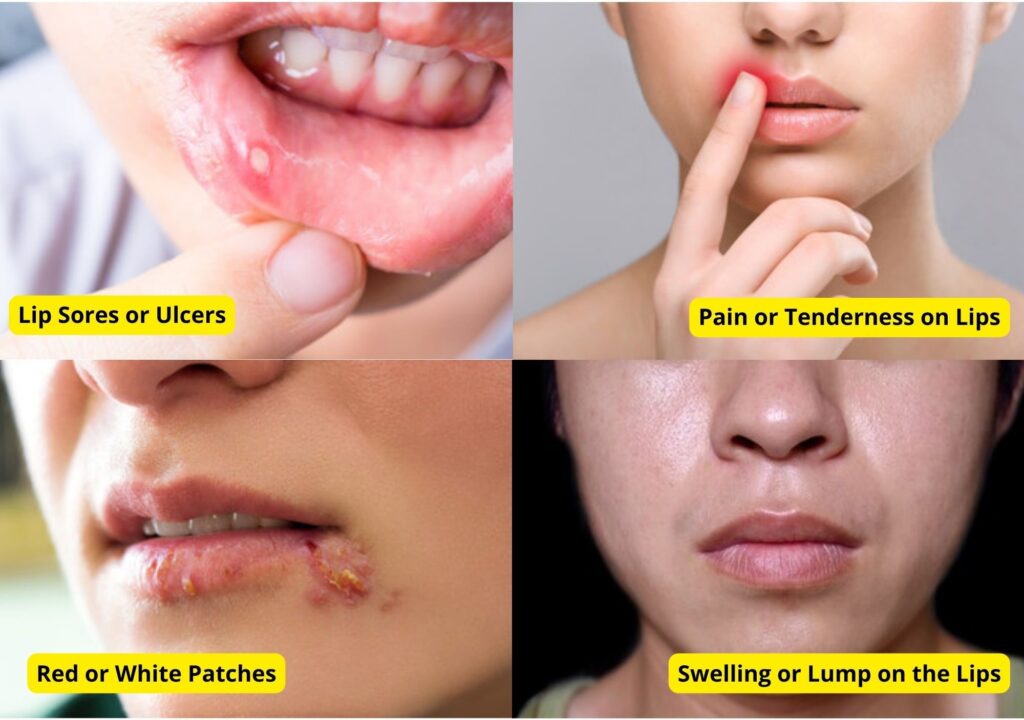
- Persistent Lip Sores or Ulcers: One of the first signs of lip cancer is a sore on the lip that doesn’t heal within a couple of weeks. In light-skinned people, it appears as a reddish patch, whereas in dark-skinned people, it appears as a dark brown or grey-colored patch. Lip cancer can look different in every person. So, if you notice any change in your lips, you should get consulted by a dentist as soon as possible.
- Pain or Tenderness on Lips: Sometimes you may feel soreness, numbness, redness, burning or itching sensation, cracking or peeling of skin, blisters, or tingling of the lips or the skin near your mouth. These symptoms can be a sign of lip cancer. If such a condition persists or gets worsens, you should see your dental healthcare provider immediately.
- Swelling or a Lump in the Lip or Mouth: Swelling or a lump in the lip or mouth can be a symptom of lip cancer. It can be caused by conditions such as a cyst, infection, or injury. If you notice a swelling or lump in your lip or mouth that doesn’t go away within a few weeks, it’s important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
- Reddish or White Patches in the Mouth: Reddish or white patches on the lip or mouth can be a symptom of lip cancer. You may notice a red bump on your lips or a white or grey patch on the tongue, gums, or inside of the cheek that can’t be scraped off and may indicate a precancerous development. This can cause a fungal infection that causes white patches in the mouth. If you notice any changes in the color or appearance of your lip or mouth or find difficulty in speaking, eating, or swallowing you must see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Thickening or Roughness of the Lips: Thickening or roughness of the skin on the lip can be a symptom of lip cancer. As the abnormal growth of cancer cells changes the texture and appearance of the skin. Lip cancer can cause thick, hard patches to form on the lip and can affect the normal smoothness and softness of the skin. This change in the texture of the skin is noticeable, and it can occur on one or both lips.
What Causes Lip Cancer?
The exact cause of lip cancer is not yet known, but there are several factors that can increase the risk of developing this condition. Here are 5 causes of lip cancer:
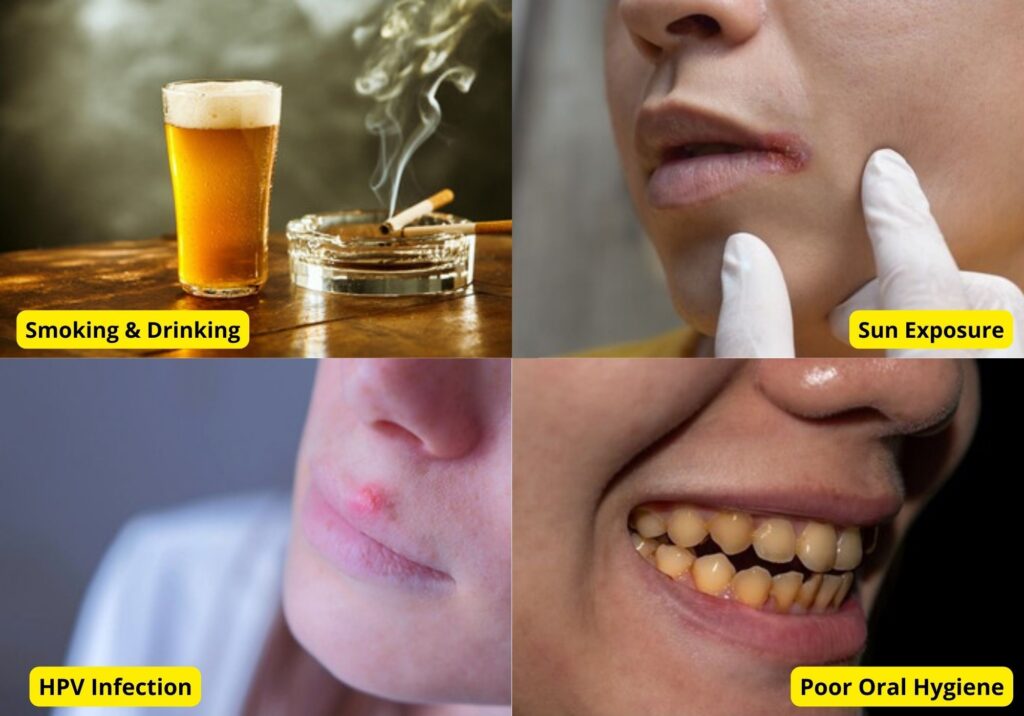
- Tobacco use (smoking, chewing): Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes and using smokeless tobacco products can increase the risk of lip cancer by damaging the DNA in the cells of the lips and surrounding tissues.
- Alcohol consumption: Alcohol can act as an irritant, especially in the mouth and throat. Cells that are damaged by the alcohol may try to repair themselves, which could lead to DNA changes that can be a step toward cancer.
- Sun exposure: Prolonged exposure to the sun’s UV rays can increase the risk of lip cancer, especially in people who have fair skin, light hair, and blue eyes.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection: Some strains of HPV can increase the risk of lip cancer, especially in people who have a weakened immune system. Most people with oral HPV infections don’t have symptoms. Because they don’t realize they’re infected, they’re more likely to transmit the virus to a partner. Some people develop oral HPV lesions — such as sores or warts on their lips, inside their mouth, or in their throat.
- Poor oral hygiene: Poor oral hygiene alone is not considered a direct cause of lip cancer, however, it can increase the risk of developing oral cancer, including lip cancer, by allowing bacteria and other harmful substances to build up in the mouth. Poor oral hygiene can also increase the risk of gum disease, eventually developing oral cancer.
Read more on 5 Common Gum Diseases – Its symptoms and Treatments
Can Lip Cancer be Treated?
Yes, it can be effectively treated. For small cancers, surgery may be a minor procedure with minimal impact on your appearance. For larger cancers, more extensive surgery may be necessary. Lip cancer treatments include the following methods:
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy
- Reconstruction surgery
Note: The choice of treatment depends on the stage and location of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. It is recommended to visit a doctor for early detection if you experience any symptoms.
You could also watch this video for more tips on taking care of your beautiful smile.
When Should You See a Healthcare Provider?
Lip cancer can be scary as it disfigures the appearance of the face. However, advanced cancer treatments and procedures in reconstructive surgery can help restore your health and appearance. You should schedule a visit with your healthcare provider anytime you notice changes in the skin on your lips or your mouth. It could indicate the early stages of lip or mouth cancer. In particular, if you develop a sore on your lip or mouth that lasts for more than two weeks, you should call your dentist immediately.

